ENT 3010 Taxa
[Site home]Sight ID characters for many taxa you'll encounter (and some you probably won't)!
Note: this page is MUCH better on a computer than a mobile device or (probably) a tablet.
| Order | Family | Common Name | Characters |
|---|---|---|---|
| Protura | Coneheads | wingless; no antennae, forelegs held as "pseudo-antennae"; minute | |
| Collembola | Springtails | wingless; forked "tail" (furcula) near end of abdomen; "peg" (collophore) on venter of 1st abdominal segment | |
| Entomobryidae | Slender springtails | slender; pronotum poorly developed; 4th tergum 2x length of 3rd | |
| Sminthuridae | Puppy springtails | globular | |
| Diplura | Two-pronged bristletails | wingless; cerci present (elongate or forceps-like); median caudal filament absent | |
| Archaeognatha (Microcoryphia) | Jumping bristletails | wingless; cerci and median caudal filament present (3 "tails"); humpbacked; large contiguous eyes | |
| Zygentoma (Thysanura) | Silverfish | wingless; overlapping thoracic nota; flattened; cerci and median caudal filament present (3 "tails"); small separate eyes | |
| Ephemeroptera | Mayflies | wings held vertically over back, hind wings (often very) reduced | |
| Ephemeridae | Common burrower mayflies | large; hind wing well developed; MP2 and CuA bent sharply downward | |
| Baetidae | Small minnow mayflies | small; hind wing tiny/absent; short paired veinlets between major veins at wing margins; median caudal filament reduced/absent | |
| Odonata | Dragonflies, damselflies | wings held spread-eagle or vertically over back; pterostigma on all wings; short bristle-like antennae | |
| == Anisoptera | Dragonflies | hind wing broader at base than fore wing; compound eyes large and close together; wings held spread-eagle at rest | |
| Aeshnidae | Darners | hind wing lacking anal loop; compound eyes contiguous | |
| Libellulidae | Skimmers | hind wing with anal loop with boot-like toe; compound eyes separated | |
| ==Zygoptera | Damselflies | all wings rougly equal in size at base, sometimes "stalked"; wings held more or less vertically over back at rest; compound eyes small and separated (hammerhead) | |
| Calopterygidae | Broad-winged damselflies | 10 or more antenodal crossveins | |
| Coenagrionidae | Narrow-winged damselflies | 2-3 antenodal crossveins; M3 arriving nearer nodus than arculus | |
| Zoraptera | Angel insects | short, 1-segmented cerci; moniliform antennae; polymorphic, may have wings or may be without | |
| Dermaptera | Earwigs | anal forceps (cerci) present | |
| Plecoptera | Stoneflies | "ladder" of veins and crossveins running diagonally across fore wings; wings held flat and extending past tip of abdomen at rest; long filiform antennae | |
| Perlidae | Common Stoneflies | cubito-anal crossveins of fore wing very close to anal cell; remnants of gills on thorax | |
| Orthoptera | Grasshoppers, crickets, katydids | saltatorial hind legs; leathery thickened fore wings (tegmina) | |
| ==Caelifera | Grasshoppers, locusts | short antennae; ovipositor unclear, not obvious | |
| Acrididae | Short-horned grasshoppers | tympana on sides of abdomen near thorax; 3-3-3 tarsal formula; short antennae | |
| Tetrigidae | Pygmy grasshoppers | pronotum extended to cover wings and abdomen | |
| Tridactylidae | Pygmy mole crickets | small; fossorial forelimbs; 2-2-1 or 2-2-0 tarsal formula | |
| ==Ensifera | Crickets and katydids | long antennae; ovipositor easily visible | |
| Gryllidae | True crickets | 3-3-3 tarsal formula; spear-shaped ovipositor; wings usually flat over back | |
| Gryllotalpidae | Mole crickets | fossorial forelegs | |
| Tettigoniidae | Katydids | 4-4-4 tarsal formula; sword-shaped ovipositor; wings usually angled over back | |
| Phasmida (Phasmatodea) | Walking sticks | prothorax shorter than meso- or metathorax; wings reduced/absent | |
| Diapheromeridae | Common walking sticks | thin and stick-like | |
| Pseudophasmatidae | Striped walking sticks | short and fat; often striped | |
| Mantodea | Mantids | elongate prothorax; raptorial forelimbs; triangular face | |
| Blattodea | Cockroaches, termites | ||
| Blattidae | Common roaches | head covered by pronotum; long filiform antennae; leathery fore wings overlapping across back | |
| Rhinotermitidae | Subterranean termites | termite-shaped; soft and white (usually); found in colonies | |
| Thysanoptera | Thrips | small; body widest in middle, tapering towards both ends; wings slender and fringed with hair | |
| Aeolothripidae | Predatory thrips | fore wings broad, with rounded tips | |
| Phlaeothripidae | Tube-tailed thrips | fore wings narrow; body dark; last abdominal segment tubular | |
| Hemiptera("Homoptera", Heteroptera) | True bugs | piercing-sucking beak | |
| == "Homoptera" | beak arises near back of head (opisthognathous); fore wings uniform in texture, held tent-like over back | ||
| Aleyrodidae | Whiteflies | wings uniformly opaque white; miniscule; often in greenhouses | |
| Aphididae | Aphids | cornicles on abdomen; soft-bodied; rounded abdomen | |
| Cercopidae | Froghoppers/spittlebugs | hind tibiae with circlet/crown of spines at tip (compare to Cicadellidae with row of spines); short bristle-like antennae; wedge-shaped head | |
| Cicadellidae | Leafhoppers | hind tibiae with comblike row of spines along length (compare to Cercopidae with crown of spines); short bristle-like antennae; wedge-shaped head | |
| Cicadidae | Cicadas | large membranous fore wings; 3 ocelli; stout-bodied | |
| Coccidae | Scale insects | Legs and antennae not apparent; anal opening with 2 triangular plates and anal cleft; usually sessile on plants | |
| Membracidae | Treehoppers | pronotum extends over wings and abdomen, often intricately shaped; often somewhat triangular in side view | |
| == Heteroptera | fore wings leathery at base, membranous towards tip | ||
| Acanthosomatidae | Parent bugs | 5-segmented antennae; body somewhat shield-shaped; scutellum usually triangular; 2-segmented tarsi (compare to 3-segmented tarsi in Pentatomidae); tibiae weakly spined | |
| Aradidae | Flat bugs | abdomen extends beyond wings in all directions; flat and bark-like in appearance | |
| Belostomatidae | Giant water bugs | strap-like respiratory tubes at end of abdomen; flattened hind legs; dorsal outline of head broken by eyes (compare to smooth outline in Naucoridae); raptorial fore legs, with proportionally large femora (not huge); elongated ovoid body; aquatic | |
| Berytidae | Stilt bugs | all legs long and thin; antennae clubbed; head not elongated; body thin and short | |
| Cimicidae | Bed bugs | wingless; flattened body; 3-segmented beak does not fit into prosternal groove | |
| Coreidae | Leaf-footed bugs | 4-segmented antennae; head narrower and shorter than pronotum; scent gland openings present between meso- and metacoxae; many parallel veins in fore wing membrane | |
| Corixidae | Water boatmen | Scoop-like front tarsi; beak usually not visible, reduced; sternum lighter than dorsum; aquatic | |
| Gelastocoridae | Toad bugs | eyes protruding; body warty, toad-shaped; aquatic/riparian | |
| Gerridae | Water striders | hind femur extends past tip of abdomen (compare to ending before tip of abdomen in Veliidae); anteapical tarsal claws; body usually dark black, wings difficult to distinguish or absent; aquatic (surface) | |
| Hydrometridae | Water measurers | slender body; head as long as thorax, with slightly rounded tip, resembling a "clown nose"; eyes on sides of head; aquatic (usually surface) | |
| Lygaeidae | Seed bugs | 4-segmented antennae; ocelli present; only 4 or 5 strong veins in fore wing membrane; all abdominal spiracles dorsal | |
| Miridae | Plant bugs | cuneus present; 4-segmented beak; ocelli absent | |
| Nabidae | Damsel bugs | very long, skinny beak; body usually elongate; raptorial fore legs; numerous closed cells around margin of fore wing membrane; can be riparian | |
| Naucoridae | Creeping water bugs | Compact, ovoid, dorsoventrally flattened; dorsal outline of head smooth (compare to broken by eyes in Belostomatidae); raptorial fore legs, with proportionally huge femora; wing membrane without veins; aquatic | |
| Nepidae | Water scorpions | long respiratory "tube" at end of abdomen; either slender-bodied & elongate with long raptorial fore legs OR compact & ovoid, resembling Belostomatidae; aquatic | |
| Pentatomidae | Stink bugs | 5-segmented antennae; usually shield-shaped; scutellum usually triangular; 3-segmented tarsi (compare to 2-segmented tarsi in Acanthosomatidae); tibiae weakly spined | |
| Reduviidae | Assassin bugs | 3-segmented beak fitting into prosternal groove; prosternal groove with transverse striations; raptorial fore legs | |
| ==Emesinae | Thread-legged bugs | threadlike mid and hind legs, raptorial fore legs; body narrow, elongated | |
| ==Phymatinae | Ambush bugs | last antennal segment swollen; 3-segmented antennae; chelate (crab-claw) fore legs | |
| Rhopalidae | Scentless plant bugs | similar to Lygaeidae, but with more than 5 parallel veins in fore wing membrane | |
| Tingidae | Lace bugs | fore wings heavily sculptured, somewhat hardened, with a "lacy" appearance; 4-segmented slightly clubbed antennae; ocelli absent | |
| Veliidae | Small water striders | hind femora ending before tip of abdomen (compare to extending beyond the abdomen in Gerridae); anteapical tarsal claws; aquatic (surface) | |
| Psocodea | Barklice, booklice, parasitic lice | thread-like antennae; "neck" between head and thorax (bark/booklice) OR small, wingless, bristly (parasitic lice) | |
| Psocidae | Common barklice | thorax broader than abdomen; broad head with long filiform antennae; wings held tent-like over abdomen | |
| Pediculidae | Body lice | thorax narrower than abdomen; compound eyes present | |
| Coleoptera | Beetles | fore wings hardened, meeting in a straight line to cover the abdomen and hind wings; prothorax usually large and distinct | |
| ==Adephaga | 1st abdominal sternum divided by hind coxae | ||
| Carabidae | Ground beetles | foretibiae with antennal cleaner; hind trochanters large and offset from femora | |
| Dytiscidae | Predacious diving beetles | flat swimming hind tarsi; short maxillary palps (compare to very long palps in Hydrophilidae); single tibial claw on hind leg; rounded on bottom ("watermelon seed") | |
| ==Polyphaga | 1st abdominal sternum undivided by hind coxae | ||
| Brentidae | Primitive weevils | rostrate; non-elbowed antennae (compare to elbowed antennae in Curculionidae) | |
| Buprestidae | Metallic wood-boring beetles | 1st and 2nd abdominal segments fused; elongate, bullet-shaped body; many metallic | |
| Cantharidae | Soldier beetles | head visible from above (compare to Lampyridae with head hidden by pronotum); elytra soft | |
| Cerambycidae | Longhorned beetles | antennae at least 0.5x body length, often much longer; eye elongate, usually wrapping around antennal bases; 3rd tarsomere on each leg bilobed | |
| Chrysomelidae | Leaf and flea beetles | short, nonclubbed antennae; 3rd tarsomere on each leg bilobed | |
| Cleridae | Checkered beetles | pronotum narrower than base of elytra; 5-5-5 tarsal formula with lobed tarsomeres, 4th typically difficult to distinguish; often pubescent | |
| Coccinellidae | Lady beetles | very rounded, domed elytra; terminal palpal segment hatchet-shaped; antennae clavate, very short | |
| Curculionidae | Weevils | rostrate; elbowed antennae (compare to Brentidae with non-elbowed antennae) | |
| ==Platypodinae | Ambrosia beetles | reddish-gold; long and rectangular; metasternum often very long (hind legs appearing as if on abdomen; squared-off end of abdomen; convex round eyes; tibiae longer than tarsi | |
| ==Scolytinae | Bark beetles | squat; long flat oval eyes; body roughly cylindrical; head somewhat withdrawn into prothorax | |
| Dermestidae | Carpet beetles | tip of abdomen extends beyond elytra; last tarsel segment longer than others; antennae capitate with 3-segmented club | |
| Elateridae | Click beetles | anterolateral corners of pronotum pointed; prosternal spine and mesosternal groove usually present | |
| Erotylidae | Pleasing fungus beetles | shiny, glabrous elytra; antennal club broad, flat, 3-segmented | |
| Geotrupidae | Round earth-boring beetles | rounded; grooved elytra; lamellate antennae; no constriction between thorax and abdomen; appear very similar to Scarabaeidae | |
| Heteroceridae | Variegated marsh-loving beetles | brown-and-tan blotched elytra; very short antennae; fossorial and strongly spined foretibiae | |
| Histeridae | Clown beetles | 2 abdominal tergites exposed beyond elytra; body greatly rounded, with grooves to receive appendages (legs, antennae); antennae short with abrupt 3-segmented club | |
| Hydrophilidae | maxillary palps longer than antennae (compare to short palps in Dytiscidae); antennae short and clubbed; flat on bottom (not "watermelon seed"); some with sternal ridge/keel | ||
| Lampyridae | Fireflies | head mostly to entirely hidden beneath pronotum when viewed from above (compare to visible head in Cantharidae); elytra soft; many (not all) with pale sternites at tip of abdomen | |
| Lucanidae | Stag beetles | 10-segmented, lamellate antennae with space between segments of club | |
| Lycidae | Net-winged beetles | elytra strongly ridged with veins and crossveins; serrate antennae | |
| Meloidae | Blister beetles | cleft tarsal claws (appears to have 4 per leg); pronotum narrower than head and elytra; elytra separated (diverging) at tips | |
| Mordellidae | Tumbling flower beetles | tip of abdomen long, pointed, extending beyond elytra; humped back | |
| Passalidae | Bess beetles | one forward-pointing horn on head; strongly grooved elytra; narrow constriction between pronotum and rest of body; lamellate antennae; shiny black bodies with short red-golden hairs closely appressed to anterior edge of thorax | |
| Scarabaeidae | Scarab beetles | lamellate antennae with compact club; 5-5-5 tarsal formula; fossorial foretibiae; strongly resemble Geotrupidae | |
| Silphidae (now Staphylinidae) | Carrion and burying beetles | antennae with noncompactible club; 5-5-5 tarsal formula; tip of abdomen extending slightly beyond elytra | |
| Staphylinidae | Rove beetles | elytra leaving (usually) at least 4 abdominal tergites exposed, often squared-off; body (usually) elongate; highly variable family, good luck | |
| Tenebrionidae | Darkling beetles | 5-5-4 tarsal formula; elytra wrapping slightly around sides of abdomen; 11-segmented antennae arising from frontal ridge anterior to eyes | |
| Trogossitidae | Bark-gnawing beetles | head visible from above; anterolateral corners of pronotum projecting, rounded | |
| Megaloptera | Dobsonflies, fishflies, alderflies | many crossveins along leading edges of wings; hind wings pleated for folding | |
| Corydalidae | Dobsonflies | plumose antennae; ocelli present; wings clear or partially smoky; sturdy mandibles, very elongated and slender (males) OR short and stout (females) | |
| Sialidae | Alderflies | small; no ocelli present | |
| Neuroptera | Lacewings and allies | many crossveins along leading edges of wings; all wings similar in size and shape | |
| Ascalaphidae | Owlflies | resemble dragonflies with long knobbed antennae | |
| Berothidae | Beaded lacewings | brown; long forked costal crossveins; small dots along wing veins | |
| Chrysopidae | Green lacewings | green/pale, unforked costal crossveins | |
| Hemerobiidae | Brown lacewings | brown; short forked costal crossveins | |
| Mantispidae | Mantisflies | elongate prothorax; numerous crossveins near leading edge of wing; raptorial forelimbs | |
| Myrmeleontidae | Antlions | resemble damselflies with short clubbed antennae | |
| Lepidoptera | Butterflies and moths | body and wings covered in small scales; mouthparts modified into coiled proboscis | |
| Cossidae | Carpenter and leopard moths | streamlined wings appearing dull and greasy; mouthparts vestigial except for palps; usually stout-bodied | |
| Erebidae | Underwings, tiger moths, tussock moths, etc. | quadrifid venation in both fore and hind wings | |
| ==Arctiinae | Tiger moths | leopard-like spots on fore wings | |
| ==Erebinae | Underwings | hind wings marked with concentric bands of contrasting colors | |
| Geometridae | Geometer moths | lined pattern on wings continuous from fore to hind wings; trifid venation in fore and hind wigns; tympana on 1st abdominal segment | |
| Lasiocampidae | Tent caterpillar and lappet moths | frenulum absent; hind wing with 2 humeral veins | |
| Noctuidae | Owlet moths | 3 medio-cubital veins reaching distal margin of hind wing; good luck | |
| Saturniidae | Giant silk moths | large lobed wings; vestigial mouthparts; stout-bodied | |
| Sesiidae | Clearwinged moths | wasp mimics (look for siphoning mouthparts); wings lack pigmented scales; fore wing narrow, hind wing broad | |
| Sphingidae | Sphinx and hawk moths | thick streamlined body; hind wings shorter than fore wings; wings often held in an inverted "V" shape along the body | |
| Yponomeutidae (incl. Attevidae) | Ermine moths | wings narrow, colorful, rolled at rest | |
| ==Papilionoidea | Butterflies | Clubbed antennae | |
| Hesperiidae | Skippers | antennae apically recurved and basally widely separated; head about as wide as thorax | |
| Lycaenidae | Blues, coppers, hairstreaks | antennae with alternating black and white bands; sturdy, hairy, extended palps; delicate wings; eye often surrounded by white ring | |
| Nymphalidae | Brush-footed butterflies | front legs generally reduced and lacking claws; monarchs and friends, wood-satyrs | |
| Papilionidae | Swallowtails and parmassians | "tail" (swallowtails) or red/orange spot (parmassians) on hind wing; cubitus in front wing appearing 4-branched | |
| Pieridae | Yellows, whites, sulphurs | well-developed front legs; bifid tarsal claws; usually white/yellow/orange with black markings | |
| Trichoptera | Caddisflies | wings held tent-like over body; wing scales modified into hairs; mouthparts not modified into coiled proboscis | |
| Mecoptera | Scorpionflies, hangingflies, fleas | rostrate "horse" head; fore and hind wings extend beyond abdomen (Mecoptera) OR laterally flattened; long saltatorial hind legs; bristly ("Siphonaptera") | |
| Bittacidae | Hangingflies | delicate, slender bodies and legs; grasping hind tarsi; resemble 4-winged crane flies | |
| Boreidae | Snow scorpionflies | small; wingless; heavily sclerotized, dark; elongate rostrum | |
| Panorpidae | Common scorpionflies | elongate rostrum; wings usually spotted or banded; body typically yellow-brown or red-brown; males with upwardly-hooked, bulbed abdomen, resembling scorpion's tail | |
| (formerly) Siphonaptera | Pulicidae | Fleas | wingless; laterally flattened; saltatorial, bristly hind legs; body covered in bristles pointing towards the head |
| Hymenoptera | Bees, ants, wasps | hamuli on costa of hind wing; triangular stigma present in fore wing ("Symphyta", some Apocrita) OR "wasp-waist" present (Apocrita) | |
| ==Symphyta | Sawflies and horntails | thorax broadly joined to abdomen; triangular stigma present in fore wing | |
| Siricidae | Horntails | front tibiae with 1 very noticeable preapical spur; ovipositor appears to begin in center of abdomen (females); tip of abdomen extended into a dorsal spur (both sexes) | |
| Tenthredinidae | Common sawflies | thick filiform antennae; tibiae with 2 preapical spurs | |
| ==Apocrita | thorax constricted before abdomen ("wasp-waist"), with first abdominal segment appressed to thorax (propodeum) and followed by a petiole | ||
| ==="Parasitica" | Parasitoid wasps | ||
| Braconidae | Braconid wasps | 1 recurrent vein in fore wing (i.e. no costal cell); no "horse head" present in fore wing (compare to horse head, 2 recurrent veins/costal cell present in Ichneumonidae); 2-segmented hind trochanters with 1st segment expanded; 2 small cells below stigma of fore wing | |
| Chalcidoidea (superfam.) | Chalcidoid wasps | venation in fore wings highly reduced or absent; wings often lightly bristly; pronotum triangular in lateral view | |
| Chrysididae | Cuckoo wasps | metallic blue/green with coarse sculpturing over body; 3 or 4 abdominal segments visible externally | |
| Evaniidae | Ensign wasps | small ovoid abdomen; abdomen attached high above hind coxae, appearing as a "signal flag" | |
| Ichneumonidae | Ichneumonid/Darwin wasps | 2 recurrent veins in fore wing (costal cell present); "horse head" present in fore wing (compare to 1 recurrent vein, no horse head in Braconidae); hind trochanters 2-segmented with 1st segment expanded | |
| ===Aculeata | Aculeate/stinging wasps | ovipositor of female modified into stinger | |
| Andrenidae | Mining bees | fore wing with free section of M straight; 2 subantennal sutures beneath each antennal socket (hard to see); in teaching collection, many golden hairs on face | |
| Apidae | Stereotypical bees | 1st segment of hind tarsi enlarged and flattened to form scopa (pollen-carrying structure); hairs, if present, branched (can be hard to see) | |
| Colletidae | Polyester bees | jugal lobe in hind wing longer than submedian cell | |
| Crabronidae | "Former Sphecidae" | pronotum anteriorly rounded; thumb-shaped lobe not reaching tegula; abdomen attached to thorax with short to very short stalk; difficult to differentiate from Sphecidae, good luck | |
| Formicidae | Ants | geniculate antennae; petiole with 1 or 2 nodes | |
| Halictidae | Sweat bees | three submarginal cells in fore wing AND basal vein in fore wing strongly arched; often metallic, but with more than 3 abdominal segments visible and not roughly sculptured (compare to Chrysididae with few abdominal segments and rough texture) | |
| Megachilidae | Mason bees | fore wings with 2 submarginal cells roughly equal in length; abdomen slightly heart-shaped; scopa on ventral side of abdomen (long rigid hairs) | |
| Mutillidae | Velvet ants | densely pubescent; females resemble ants without nodes; felt lines on 2nd abdominal tergum; males winged, females unwinged | |
| Pompilidae | Spider wasps | hind femur reaching tip of abdomen; tibiae with 2 large apical spurs; mesopleuron bisected by transverse suture; can be mistaken for Sphecidae if abdomen petiolate | |
| Scoliidae | Scoliid wasps | many small longitudinal wrinkles on wings; wings usually darkened; no closed cells at apex of fore wings (veins end before apex of wing) | |
| Sphecidae | Thread-waisted wasps | stalked abdomen, with petiole composed of only sternite; middle tibiae with 2 apical spurs; pronotum rounded anteriorly, with thumb-shaped lobe not reaching tegula; difficult to differentiate from Crabronidae and some Pompilidae) | |
| Thynnidae/Tiphiidae | Flower wasps | 2 posteriorly pointing lobes on mesosternum, between trochanters of middle legs | |
| Vespidae | Stereotypical wasps | fore wings folded longitudinally at rest ("hot dog"); posterior margin of pronotum distinctly U-shaped | |
| Diptera | True flies | fore wings membranous; hind wings reduced to club-like halteres | |
| =="Nematocera" | antennae with >6 distinct segments; usually slender, frail-bodied | ||
| Bibionidae | March flies | ocelli present; antennae short, stout, low on face; usually black-bodied and black-winged | |
| Ceratopogonidae | No-see-ums | very small; ocelli absent; costa and Rs well-developed, other veins weak | |
| Chironomidae | Midges | plumose antennae; M unforked; chewing mouthparts | |
| Culicidae | Mosquitoes | plumose antennae; scales on wing veins; hump-backed thorax; piercing-sucking long proboscis | |
| Ptychopteridae | Phantom crane flies | one anal vein reaching wing margin (compare to two in Tipulidae); halteres with small process at back | |
| Simuliidae | Black flies | broad wings; posterior wing veins poorly developed | |
| Tipulidae | Crane flies | V-shaped suture on mesonotum; two anal veins reaching wing margin (compare to one in Ptychopteridae); prominent halteres | |
| ==Brachycera | antennae with 3-4 segments; last antennal segment annulated/stylate | ||
| Asilidae | Robber flies | beard (mystax) on face; vertex sunken | |
| Bombyliidae | Bee flies | long proboscis; R2+3 and R4 sinuate; usually fuzzy-bodied | |
| Dolichopodidae | Long-legged flies | small, delicate, long legs; Rs 2-branched; often metallic | |
| Stratiomyidae | Soldier flies | circular discal cell near wing center | |
| Tabanidae | Horse/deer flies | R4 and R5 enclose wing tip in Y-shape; third antennal segment elongate, annulated; large compound eyes | |
| ===Cyclorrhapha | Higher flies | antennae with 3 segments and arista | |
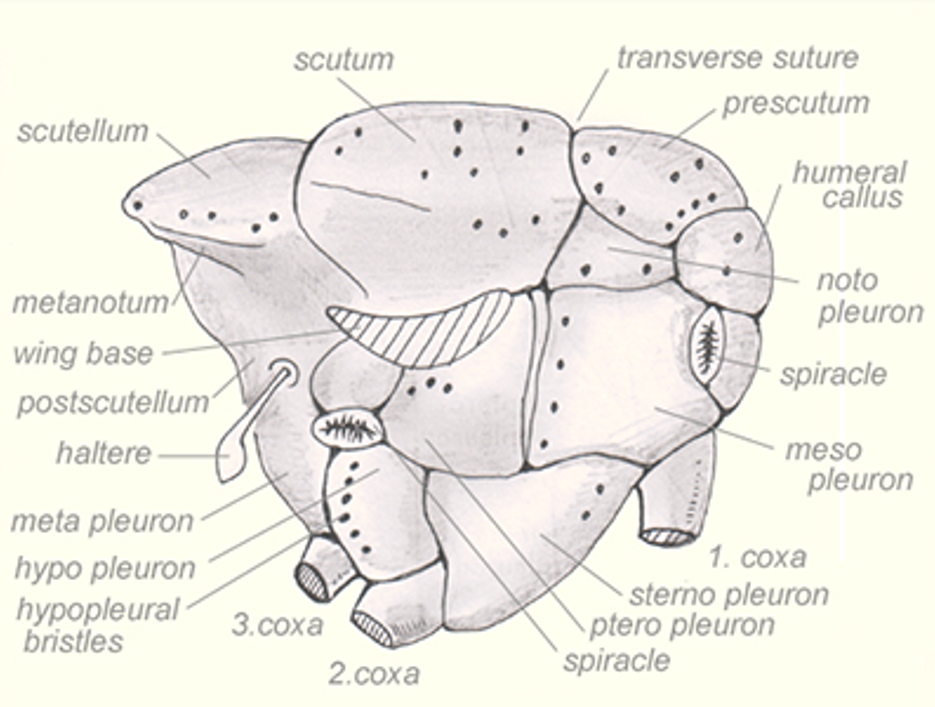
| Calliphoridae | Blow flies | hypopleuron and pteropleuron with bristles; notopleuron with 2 bristles; arista plumose to tip; postscutellum absent | |
| Hippoboscidae | Keds | flat and tick-like; coxae widely separated | |
| Muscidae | House flies and kin | hypopleuron without bristles; arista plumose to tip; Cu2 + 2A never reaches wing margin | |
| Oestridae | Bot flies | large; hairy; mouthparts absent | |
| Phoridae | Scuttle flies | humpbacked; hind femora laterally compressed | |
| Sarcophagidae | Flesh flies | arista bare OR plumose only in basal half; hypopleuron and pteropleuron with bristles; notopleuron with 4 bristles | |
| Syrphidae | Hover flies | spurious vein bisecting r-m crossvein; abdomen usually dorsoventrally flattened; often mimic wasps | |
| Tachinidae | Parasitic flies | postscutellum bulging; abdomen with stout bristles; arista bare and unbranched; hypopleuron and pteropleuron with bristles | |
| Ulidiidae | Picture-winged flies | costa unbroken near end of Sc; wings often patterned; somewhat slender, often orangeish |
| Hypopleuron | Pteropleuron | Notopleuron | Postscutellum | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Muscidae | no | X | X | absent/inconspicuous |
| Calliphoridae | yes | yes | 2 | absent/inconspicuous |
| Sarcophagidae | yes | yes | 4 | absent/inconspicuous |
| Tachinidae | yes | yes | X | bulging |